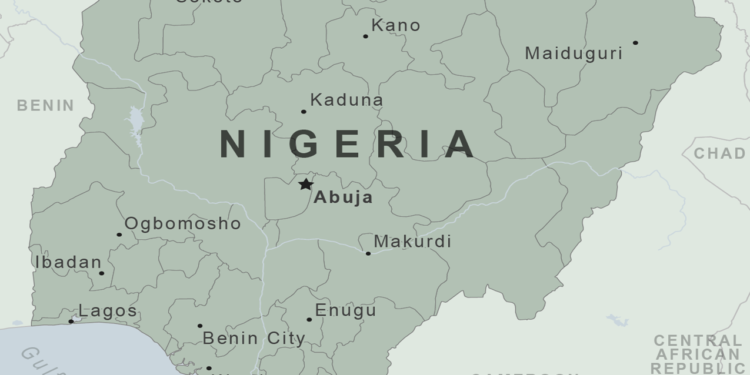
Nigeria, country located on the western coast of Africa. Nigeria is the most important country politically and economically in West Africa. It is richer than all other West African nations and holds considerable power. The national capital is Abuja, in the Federal Capital Territory, which was created by decree in 1976. Lagos, the former capital, retains its standing as the country’s leading commercial and industrial city.
Nigeria has a lengthy and intricate history that dates back thousands of years, encompassing the founding of ancient civilizations, the slave trade, British colonization, and independence. The Niger River, which flows across the nation, inspired the name Nigeria. It is said that British writer Flora Shaw, who subsequently married British colonial administrator Baron Frederick Lugard, came up with this name in the late 1800s. It’s unclear where the term Niger came from, although some believe it is most likely an alteration of the Tuareg name “egerew n-igerewen” used by Tuareg people living along the middle reaches of the river before European colonization.
Throughout history, the territory that is now known as Nigeria has seen the rise of several kingdoms, states, empires, and caliphates. According to archeological evidence found in different regions of Nigeria, humans have lived in sections of the nation since the Palaeolithic, often known as the Old Stone Age (500,000–9000 B.C.). These people appear to have been geographically and culturally close to the current occupants.
The Hausa, Kanuri, Bolawa, Ngizim, Menga, Margi, Buduma, Kotoko, and Fulani were the most populous groups in the north when they merged through commerce, jihad, and conquest in the 19th century. Out of all these peoples, the Fulani, the Hausa, and the Kanuri were involved in the process of establishing empires and states. The inhabitants of Kanem, on the eastern portion of Lake Chad, where a kingdom made up of numerous petty kingdoms arose in the ninth century, were closely related to the Kanuri people. The Sefawa first appeared around AD 774 and eventually took over the whole Lake Chad region.

The region of the Bauchi Plateau in the province of Adamawa is where ethnic heterogeneity peaked. It appears that most ethnic groups to the south of Borno and Hausa region have not arranged themselves into tightly knit governments. The Jukuns (Kwararafa) of the Gongola Benue lowlands, the Igala, the Igbira-Panda, Nupe, the Oyo Yoruba of the savanna belt, the Borgawa, and the Edo were grouped into relatively strong kingdoms and empires in this politically divided area.
Yorubaland, which is situated in the southern regions of Nigeria, is thought to have existed as early as 500 BC according to artifacts from Ifẹ̀. Every Yoruba kingdom believed that one or more of its founders came from Ife. Each yoruba kingdom served as the political power unit. However, cultural identification extended outside the monarchy to encompass dialect-speaking sub-ethnic groups. Oyo, Egba, Egbado, Ijebu, Ijesa, Ekiti, Ondo, Akoko, and Owo were the main sub-ethnic groupings of the Yoruba. The Oyo empire was the Yoruba kingdom that was most successful in gaining power. It made use of its advantageous location to amass a cavalry force that allowed it to rule not only the Oyo region but also the neighboring regions of Borgu and Nupe, Egbaland and Egbado, Dahomey, and Porto Novo.
The Edo group owns the heartlands of the Benin Kingdom (and later Benin Empire). It’s quite likely that the kingdom hasn’t existed for more than a thousand years. With some degree of confidence, the customs upheld by the monarchy itself may be traced back to the 13th century. The Igbo in eastern Niger and the inhabitants of the Delta area are located to the south of the Edo and Yoruba. The peoples of the Delta area are home to a variety of social and political structures. These comprise the broken societies of the Ukwuani, Urhobo, Isoko, and Ijo, as well as the kingdoms of Aboh and Itsekiri.
It is common to classify the Igbo people as belonging to decentralized societies, as the Igbo people did not live in a unified state or develop a state structure of significant magnitude. Nevertheless, Igbo society and culture benefited from a fundamental homogeneity of pattern as well as social and cosmological concepts.
After the British “conquered” Lagos in 1861, the Lagos Colony was established. A governor oversaw the colony together with a legislative council.
Modern Nigeria dates from 1914, when the British Protectorates of Northern and Southern Nigeria were joined.The country became independent on October 1, 1960, and in 1963 adopted a republican constitution but elected to stay a member of the Commonwealth.
Nigeria has a diverse geography, with climates ranging from arid to humid equatorial. The country is a patchwork of distinctive regions, including deserts, plains, swamps, mountains, and steamy jungles. It has one of the largest river systems in the world, including the Niger Delta, the third largest delta on Earth.
There are an estimated 250 ethnic groups in Nigeria. However, Nigeria’s most diverse feature is its people. Hundreds of languages are spoken in the country, including Yoruba, Igbo, Fula, Hausa, Edo, Ibibio, Tiv, and English. The country has abundant natural resources, notably large deposits of petroleum and natural gas.
Nigeria is an African country on the Gulf of Guinea. It has many natural landmarks and wildlife reserves. It has various protected areas such as Cross River National Park and Yankari National Park, both of which have waterfalls, dense rainforests, savanna and rare primate habitats.