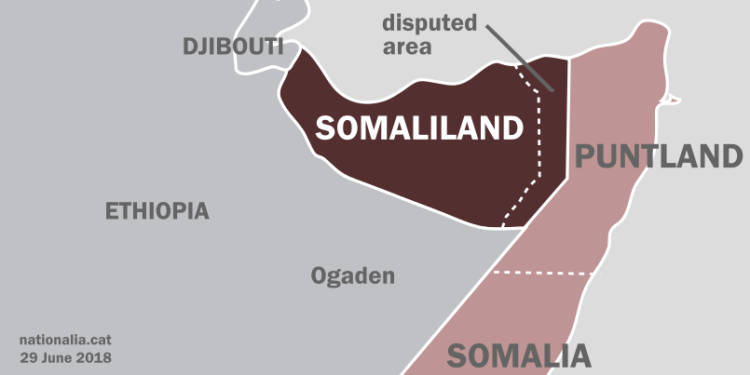
Somaliland is part of Somalia and the larger Horn of Africa region. It has hundreds of miles of coastline along the Gulf of Aden to the north, and it borders Ethiopia to the south and west and Djibouti to the northwest. Puntland, a semiautonomous state of Somalia that lies due east, disputes some of Somaliland’s territorial claims. In 2001, 10 years after breaking away from Somalia, Somaliland still was not internationally recognized as an independent country. Undeterred, the government held a referendum that year, the results of which clearly showed that Somaliland’s inhabitants supported the region’s claim of independence. Even so, while Somaliland aims at splitting Somalia into independent states, Puntland fights for the reestablishment of a federal Somali state. As such, they are always in constant arguments.
Although Somaliland is strategically located in geopolitical and trade terms with key global military and shipping interests in the region that could help the US counter China. In particular, the Bab-el Mandeb strait in the Gulf of Aden between Somaliland’s Berbera port, Djibouti, and Yemen is widely seen as a critical shipping choke point for moving goods and military wares in the sub-region. This territory, officially a unitary republic of over 6 million inhabitants and a land area of 176,120 square kilometers, boasts of all the trappings of an independent country, such as its own president elected every five years, a respectable currency, the Somaliland Shilling, and a total GDP of $3.782 billion, according to a 2022 estimate. Hence, the following sections pointed out will enlighten the readers on Somaliland in relation to the geopolitical events in the Horn of Africa, the region’s political economy, and its effects on the overall development.
Somaliland and the Geopolitics of the Horn of Africa
Somaliland is a former British protectorate that joined the rest of Somalia on 1 July 1960. Between 1969 and the early 1980s, Mohamed Siad Barre’s military government imposed a system of “scientific socialism,” which was characterized by the nationalization of banks, insurance firms, oil companies, and large industrial firms; the establishment of state-owned enterprises, farms, and trading companies; and the organizing of state-controlled cooperatives. In the chaos that followed Barre’s departure, Somaliland declared its independence and has since rebuilt the city and created its own currency, institutions, and security structures. This is often contrasted to Somalia, which collapsed into anarchy for decades and still faces many challenges, including from Islamist militants, and does not hold direct elections (BBC, 2024). Accordingly, in spite of mediation efforts by Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, Djibouti, and the United Kingdom, the two sides have not moved any closer to the fundamental question of whether to remain united or separate.
Some observers, such as Adam Daud Ahmed, a political and security analyst in the Horn of Africa, argue that in direct contrast to the general instability characterizing the region, Somaliland has maintained a stable and democratic governance model since declaring independence from Somalia in 1991. Likewise, Somaliland has demonstrated extraordinary resilience and resolve to build a stable and democratic society, achieving remarkable milestones along the way. As well, in a book, ”When There Was No Aid: War and Peace in Somaliland,” by Sarah G. Phillips, an Associate Professor in the Department of Government and International Relations at The University of Sydney. Phillips noted that there are other intriguing ingredients behind Somaliland’s relative success, none of which fit within a technocratic frame. Firstly, the elite all went to the one secondary school, forging trusted personal relationships with each other through the old school tie; secondly, apprehension of a conflict returning helps keep the peace.
Withal, many countries have encouraged the breakaway state’s elections and economic development, but none have recognized Somaliland. While some experts see historical and geopolitical reasons for countries such as Ethiopia and Kenya to take this step, others say the African Union (AU) would have to be the first to do so. In 2024, Ethiopia and Somaliland sign a memorandum of understanding for landlocked Ethiopia to use one of Somaliland’s ports. Somalia describes the agreement as an act of “aggression.”. Somalia, angered by the deal, expelled Ethiopian diplomats, pushed the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops under the African Union peacekeeping mission in Somalia (ATMIS), and agreed to the deployment of Egyptian forces in their stead, risking further destabilization of the already volatile Horn of Africa region. Hargeisa is also hopeful U.S. President-elect Donald Trump will be favorable to its cause. While former diplomats in charge of Donald Trump’s Africa policy want him to include recognition of Somaliland’s independence in his program, reports said. According to the BBC, powerful and influential Republicans are pushing for the same thing, including Congressman Scott Perry, who last month introduced a bill proposing formal US recognition for Somaliland.
Somaliland’s Political Economy: State of Affairs
The Somaliland economy is driven by the private sector, according to the World Bank’s report in January 2016. The international financial institution points out that, like most other economies in the world, the government footprint is limited, amounting to under 10 percent of the gross domestic product (GDP). Gemstones and industrial minerals that are abundant in Somaliland include any kind of gemstones. There are also plenty of other minerals in Somaliland, such as industrial minerals like iron ore, titanium, aluminum, tungsten, tin, and galena, and other rare earth metals like columbite tantalite, molybdenum, and many other rare minerals that are only found in a few places in the world. Due to the weakness of local production, consumer as well as producer goods are mostly imported from foreign countries. Imports principally through Berbera Port are classified into food items, i.e., sugar, rice, wheat flour, wheat, cooking oil, dates, pasta, biscuits, etc. And nonfood items including petrol, diesel, clothes, cars/trucks, spare parts, cigarettes, soap, building materials, etc. However, another import channel is Wajale customs on the Ethiopia-Somaliland border, where food and nonfood items, primarily Kat, are imported.
Besides, the economy of Somaliland largely depends on livestock and agriculture. In 2019, Somaliland had a gross domestic product (GDP) of about US$ 2 billion, most of which it received in remittances from Somalilanders working abroad, and a GDP per capita of US$ 950, which is one of the lowest in the world. Livestock is the main export, which is shipped to neighboring Djibouti and Ethiopia, as well as to Gulf states such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman. Somaliland generates an estimated US$ 250 to US$ 350 million per year of hard currency. However, in relation to the trade, a few prominent businessmen dominate the Somaliland economy, monopolizing much of the trade in livestock, food, and construction materials, as well as the clearance, retail, wholesale, and transportation services, leaving no room for smaller traders and merchants. Moreover, the problem with these smaller traders is that they do not generate enough capital to grow into large-scale enterprises or provide employment opportunities beyond family members. In addition, the sector appears to lack the ability to initiate original business ideas. Therefore, Somaliland constitutes what we can call an ‘oligopolistic state,’ referring to the small number of firms and elites that, after independence—and through discreet cross-border business networks and unaccounted financial flows—colluded, either explicitly or tacitly, to limit competition and restrict the authority of the state in order to achieve above-normal market returns and protections.
In the Burco conference that was declared on Somaliland’s independence on 18 May 1991, which was based on the legal and historical grounds of British Somaliland on 26 June 1960, all the major Somaliland-inhabited tribes, including the Harti, Isaaq, Isse, and Gedabursi, etc., attended. But perhaps due to the conflict-affected situation, the Burco declaration and the Harti delegates were not fully satisfied at that time, and later they had interpreted the conference into a peace and reconciliation conference rather than a government and independence conference from the collapsed Somalia. For the Harti elites, it was just a matter of capacity and a weakened position that waits for the first chance. Somaliland maintains a hybrid political order that integrates traditional political institutions into its governance system. The system stems from the 1993 inter-clan conferences, where the current structure of governance was put in place with the establishment of the Guurti, or the upper house of parliament, mainly taken by representatives from traditional clan leaders, as the house retains mandate for all matters concerning dispute settlements. However, seen as an obstacle to the progression of the democratization process, clans play a major role in the political discourse.
Political economy is about how politics affects the economy and the economy affects politics. The political economy thus begins with the observation that actual policies are often quite different from “optimal’’ policies, the latter defined as subject to technical and informational, but not political, constraints. The Somaliland constitution limits the number of political parties to no more than three. In the region, the constitution also makes it unlawful for any political party to be based on regionalism or clannism. The selection process for the three political parties eligible to participate in national elections is set in the Law for Regulation of Political Associations and Certification of Political Parties (Law No. 14). Political associations would compete in local council elections, with the three receiving the most votes eligible to stand for subsequent elections. While the three political parties are the Peace, Unity, and Development Party; Waddani; and For Justice and Development.
In contrast with southern Somalia, Somaliland has enjoyed relative peace since the late 1990s. This is when feuding within Somaliland’s largest clan—the Isaaq—ended in a peace settlement, brokered by some non-Isaaq clans. The previous armed conflict within the Isaaq was based on who should control the political economy, which was weak at the time. Today, the Isaaq clan controls much of the political and economic landscape. This may intensify tensions, especially if minority clans feel sidelined. The eastern parts of the Sool and Sanaag regions, as well as the district of Buhoodle in Togdheer, are primarily inhabited by the Dhulbahante and Warsengeli sub-clans of the Darod clan. They have been subject to a long-running territorial contest between Somaliland and Puntland. At the same time, its reputation for orderly polls and relatively consensual politics has come under strain recently, and disputes among politicians caused a two-year delay of the presidential vote. However, in the end, Somaliland’s institutions and political establishment largely withstood the stress test. The results saw Abdirahman Mohamed Abdullahi “Cirro,” leader of the Waddani party, secure the presidency with 64 percent of the vote, defeating incumbent Muse Bihi of the Kulmiye party.
In September 2016, the Somaliland government agreed to a thirty-year concession with DP World, the Dubai-based ports operator, to develop and operate the port of Berbera. The US$440 million expansion will transform Berbera—already a significant hub for the Horn of Africa’s regional livestock trade—beyond recognition. The two-phase development incorporates plans for a new 400m quay, a 250,000 m² yard, and upgrades to the city’s airport. The Berbera corridor will expand port access for neighbouring Ethiopia, which has a 19 per cent stake in the development., In addition, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has committed over US$100 million in additional investment to upgrade the 250 km road connecting the port with Hargeisa, Somaliland’s capital, and Togwajale, a town astride the border with Ethiopia. Likewise, this investment has enormous potential to act as a driver of inclusive development, generating formal and informal jobs and stimulating a range of economic sectors in a geopolitically crucial region characterized by poverty, unemployment, and inequality as well as radical Islam and violent conflict.
To the contrary, in recent times, the new livestock-exporting guidelines imposed by the Federal Government of Somalia have affected the livestock markets in Burao and Hargeisa. Products made by small-scale factories in Burao are no longer marketed in Puntland or other federal member states. Also, the closure of key trade corridors, including the recent one linking Erigabo to other regions, has disrupted vital economic connections, severely impacting Somaliland’s recovery. While the absence of international recognition has profound implications for Somaliland’s economic development. In an interview in September 2024, the former interior minister, Mohamed Kahin Ahmed, explained that the region is unable to access international financial markets or secure development aid from global institutions such as the World Bank and International Monetary Fund. However, the region has benefited significantly from foreign aid in various forms, provided by countries, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the diaspora. While peace did not require vast external financing. There was none available anyway at the time, save for remittance flows to Somaliland families, totaling an estimated $500–900 million annually by 2019.
The Path to a New Future
Despite its challenges, including economic constraints and limited international support, Somaliland has managed to create a functioning state with essential services and governance structures. The region’s successes highlight the potential for a peaceful and democratic alternative in a historically tumultuous area. All the same, reform of key sectors is needed to sustain revenue generation and create a more competitive economy, according to the World Bank. At length, in a study titled “The Role of Business in Maintaining Peace in Somaliland’’ by Musa Ahmed M. and Cindy Horst in 2017, it is argued that foreign private actors are important to attract capital, skills, and knowledge and could boost the local economy. They could also assist in improving the state’s autonomy from domestic business elites. As well, considering the political culture and weak institutional capacity in Somaliland, foreign actors may threaten the peace by affecting the delicate power balance between local actors and by introducing transnational interests.
While building the capacity of the human resources of the state, developing new policies that worked in the interest of the citizens, and implementing the existing policies would be key factors that would decisively affect the state’s efforts to develop and prosper. Needless to say, Somaliland desperately needs to establish responsible governance institutions that provide social services to those in need across the country. However, Somaliland’s stability and democratic governance contrast sharply with Somalia’s instability and the authoritarian regimes throughout the rest of the Horn. This is a chance to appear as a beacon of democracy in a sea of autocracies in the region.
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
This article expresses the views and opinions of the author and does not necessarily reflect the views of Qiraat Africa and its editors.